Featured Health Topics
Sciatica Causes
The origins and risk factors of sciatica can be related to several underlying causes.
Back Strengthening Exercises
Back strengthening exercises primarily target core muscles like the abs and hips, providing vital support and minimizing spinal strain.
Treatment for Neck Pain
Neck pain treatment includes rest, pain relievers, physical therapy, exercises, ergonomic adjustments, and in severe cases, surgery.
Neck Strain: Causes and Remedies
Spotlight on your health
Sciatica Causes and Symptoms Video
Sciatica is leg pain caused by a problem in the low back. Watch an animated video that details the causes and symptoms of sciatica.
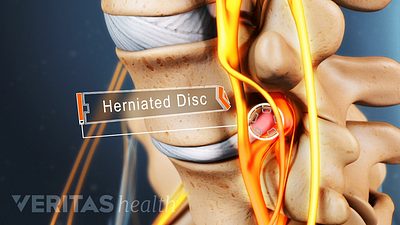
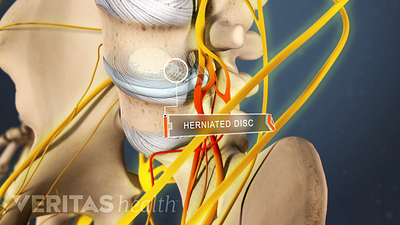
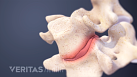
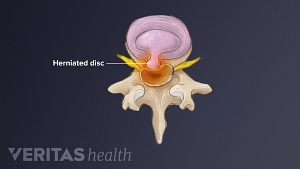
Lumbar Herniated Disc Video
A herniated disc in the lumbar spine can put pressure on spinal nerve roots, causing pain in the lower back or legs.
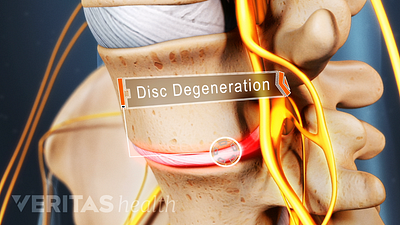
Cervical Degenerative Disc Disease Video
Neck pain and stiffness may be the result of cervical degenerative disc disease. While more common in the lumbar spine, DDD can occur in the neck as well.
Video: 2 Walking Tips to Avoid Sciatica Pain
Walking can help to alleviate sciatica pain, but only when done correctly. Use these two tips to make sure you're getting the most out your walks.
Editors Top Picks
Relieve sciatica pain and prevent future flare-ups by stretching and strengthening your lower back, abdominal, and thigh muscles with these 3 simple exercises.
Avoid activities that involve bending, twisting, lifting, and exercise with jarring motions to prevent herniated disc pain from becoming worse.
Pain in the shoulder blade region is fairly common and can be quite painful and limiting. It can have many causes, ranging from a muscle strain to a more serious condition that requires immediate medical attention.
Leg weakness may cause sudden buckling, an unsteady gait, and possible falls. Here are a few possible conditions that may cause weakness in your legs.