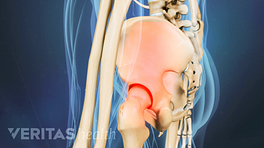
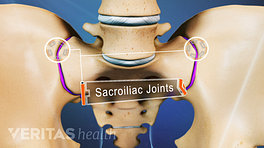
If you have sacroiliac (SI) joint pain that has not subsided with first-line treatments, your doctor may suggest radiographic and imaging tests to investigate the cause of pain further and rule out serious medical conditions.
A broad variety of radiographic and imaging tests are available to help identify pain caused by SI joint dysfunction.
In This Blog:
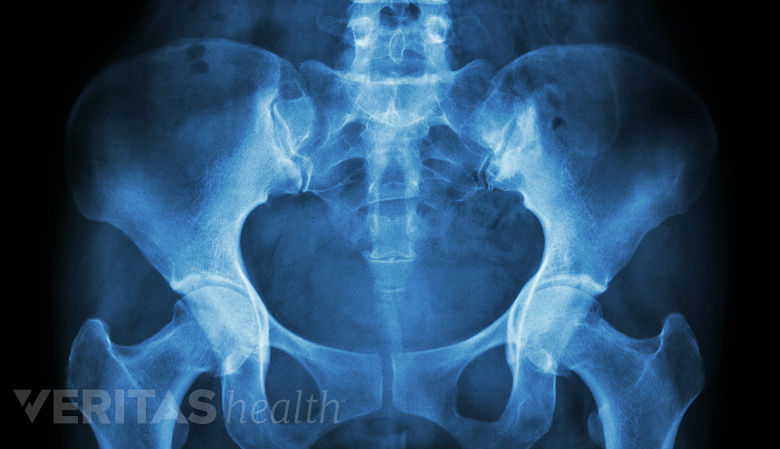
X-ray
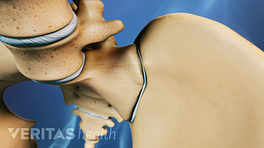
X-rays may detect fractures or degenerative changes in the SI joint.
An x-ray is an imaging technique that uses electromagnetic radiation to provide a general overview of the spine. SI joint x-rays can help detect conditions affecting the joint, such as fractures and degenerative changes, including but not limited to joint space narrowing and bone spurs. 1 Thawrani DP, Agabegi SS, Asghar F. Diagnosing Sacroiliac Joint Pain. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2019;27(3):85-93. http://doi.org/10.5435/JAAOS-D-17-00132
X-rays are often the first test used to diagnose SI joint dysfunction, as they are quick and easy to perform and help the physician determine if more detailed medical imaging, such as computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan, is needed. 2 Lee A, Gupta M, Boyinepally K, Stokey PJ, Ebraheim NA. Sacroiliitis: A Review on Anatomy, Diagnosis and Treatment. Advances in Orthopedics. 2022. http://doi.org/10.1155/2022/3283296
CT scan
A CT scan helps identify joint erosion.
A CT scan is a radiological imaging technique that creates two-dimensional images of the body in horizontal and cross-sectional (sliced) planes. 3 Hermena S, Young M. CT-scan Image Production Procedures. [Updated 2022 Aug 8]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK574548/#_NBK574548_pubdet_ CT scans of the SI joint help visualize erosive changes in the joint and hardening and/or thickening of the bone (subchondral sclerosis). 1 Thawrani DP, Agabegi SS, Asghar F. Diagnosing Sacroiliac Joint Pain. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2019;27(3):85-93. http://doi.org/10.5435/JAAOS-D-17-00132
It is important to note that a CT scan is generally not recommended for pregnant women and children under 10 due to potential tissue damage to the developing organs. 4 Patel PR, De Jesus O. CT Scan. [Updated 2022 Jan 5]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2022 Jan. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK567796/
MRI scan
MRI can detect early inflammation and bone changes.
MRI is a highly sensitive and specific imaging technique that yields comprehensive images of the structure, function, and composition of tissues in the body. 5 Balasubramanya R, Selvarajan SK. Lumbar Spine Imaging. [Updated 2022 Mar 9]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2022 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK553181/ , 6 Chan RW, Lau JYC, Lam WW, Lau AZ. Magnetic resonance imaging. In: Encyclopedia of Biomedical Engineering. Elsevier; 2019:574-587. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-801238-3.99945-8 MRI scans of the SI joint can help detect early inflammation, erosive changes, arthritic changes, and soft-tissue problems. MRI scans can also rule out other sources of pain or serious medical conditions in the SI joint area. 1 Thawrani DP, Agabegi SS, Asghar F. Diagnosing Sacroiliac Joint Pain. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2019;27(3):85-93. http://doi.org/10.5435/JAAOS-D-17-00132
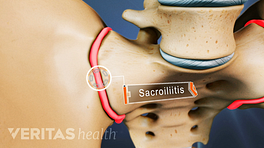
Bone scan
A bone scan is a diagnostic test that uses nuclear imaging. This scan can help identify and track the severity of bone-related problems, including cancers, arthritis, infections, fractures, and unexplained bone pain.
Bone scans of the SI joint help identify stress fractures, inflammatory changes, infections, and tumors. 1 Thawrani DP, Agabegi SS, Asghar F. Diagnosing Sacroiliac Joint Pain. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2019;27(3):85-93. http://doi.org/10.5435/JAAOS-D-17-00132
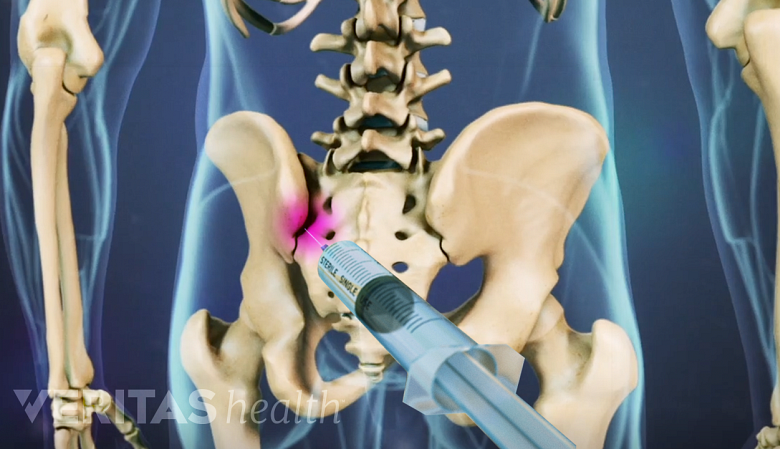
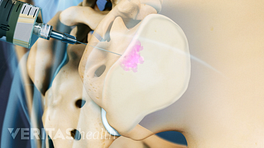
Diagnostic injection tests with ultrasound or fluoroscopy
SI joint blocks may be used to identify SI joint pain.
Diagnostic SI joint injections, also called SI joint blocks, use ultrasound or fluoroscopy (real-time x-ray imaging) to pinpoint pain originating from the SI joint. The test involves delivering a small amount of anesthetic and/or corticosteroid directly into the SI joint and monitoring the patient’s pain and other symptoms. Significant pain reduction (>75%) after the test typically confirms that the pain originates from the SI joint. 7 Kao MC, Chuang CW, Hung SK, Pan PT. Diagnosis and interventional pain management options for sacroiliac joint pain. Tzu Chi Medical Journal. 2019;31(4):207-210. http://doi.org/10.4103/tcmj_54_19 Some researchers consider SI joint blocks as a gold standard test to identify SI joint pain, but in 20% to 50% of patients, these tests may yield false-positive results, which may lead to an inaccurate diagnosis. 8 Nejati P, Sartaj E, Imani F, Moeineddin R, Nejati L, Safavi M. Accuracy of the Diagnostic Tests of Sacroiliac Joint Dysfunction. J Chiropr Med. 2020;19(1):28-37. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcm.2019.12.002
Injections are minimally invasive and are usually considered a safe and low-risk procedure. However, as with any injection procedure, there is always a risk of side effects or potential complications, such as allergic reactions, nerve damage, bleeding, or infection, which must be discussed in detail with the physician before considering these tests.
Learn more:
- 1 Thawrani DP, Agabegi SS, Asghar F. Diagnosing Sacroiliac Joint Pain. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2019;27(3):85-93. http://doi.org/10.5435/JAAOS-D-17-00132
- 2 Lee A, Gupta M, Boyinepally K, Stokey PJ, Ebraheim NA. Sacroiliitis: A Review on Anatomy, Diagnosis and Treatment. Advances in Orthopedics. 2022. http://doi.org/10.1155/2022/3283296
- 3 Hermena S, Young M. CT-scan Image Production Procedures. [Updated 2022 Aug 8]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK574548/#_NBK574548_pubdet_
- 4 Patel PR, De Jesus O. CT Scan. [Updated 2022 Jan 5]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2022 Jan. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK567796/
- 5 Balasubramanya R, Selvarajan SK. Lumbar Spine Imaging. [Updated 2022 Mar 9]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2022 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK553181/
- 6 Chan RW, Lau JYC, Lam WW, Lau AZ. Magnetic resonance imaging. In: Encyclopedia of Biomedical Engineering. Elsevier; 2019:574-587. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-801238-3.99945-8
- 7 Kao MC, Chuang CW, Hung SK, Pan PT. Diagnosis and interventional pain management options for sacroiliac joint pain. Tzu Chi Medical Journal. 2019;31(4):207-210. http://doi.org/10.4103/tcmj_54_19
- 8 Nejati P, Sartaj E, Imani F, Moeineddin R, Nejati L, Safavi M. Accuracy of the Diagnostic Tests of Sacroiliac Joint Dysfunction. J Chiropr Med. 2020;19(1):28-37. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcm.2019.12.002