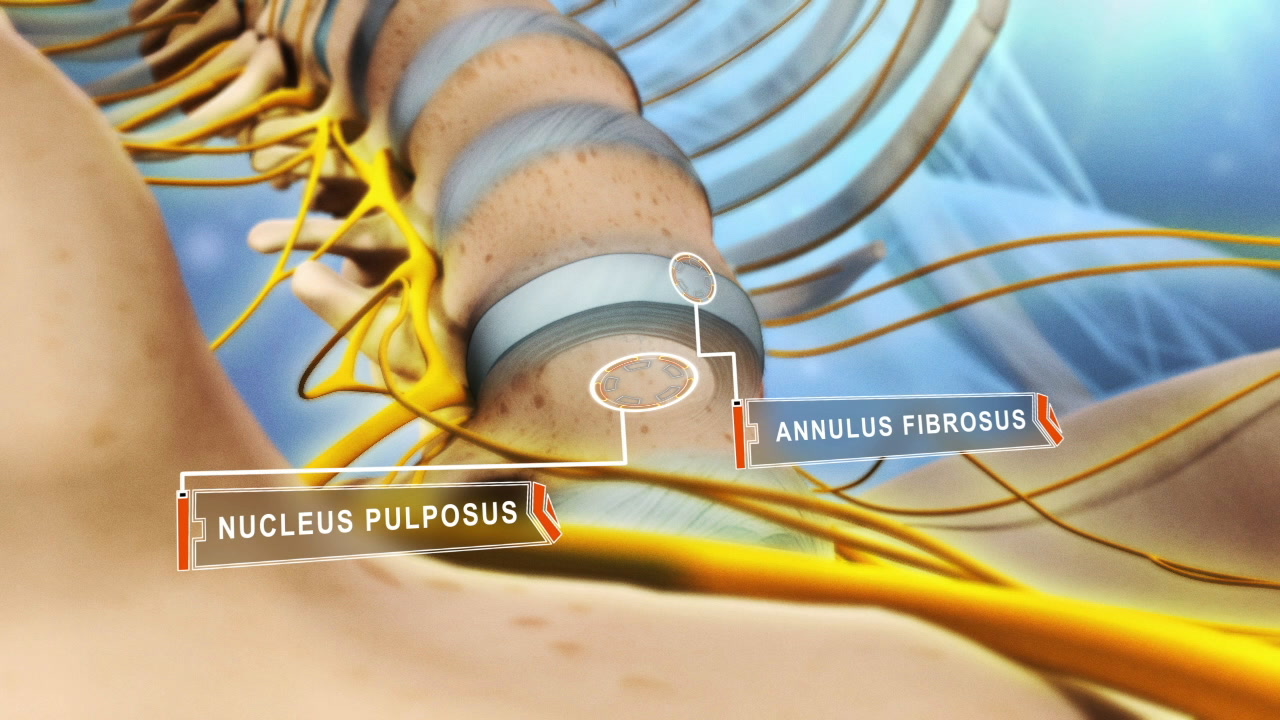
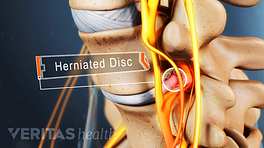
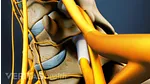
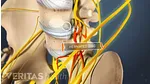
A herniated disc occurs when the inner gel-like core (nucleus pulposus) of a spinal disc pushes through a tear or weak point in the tough outer layer (annulus fibrosus). A lumbar disc herniation occurs in the lower back (lumbar spine), and most commonly develops at the L4-L5 and L5-S1 spinal motion segments, located toward the base of the lower back. 1 Al Qaraghli MI, De Jesus O. Lumbar Disc Herniation. [Updated 2023 Aug 14]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK560878/ , 2 Dydyk AM, Ngnitewe Massa R, Mesfin FB. Disc Herniation. [Updated 2023 Jan 16]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK441822/
A herniated disc becomes a source of pain and discomfort if it irritates or compresses nearby structures, such as a spinal nerve root.
The size of the herniation does not always correlate with the intensity of symptoms. A small herniation might cause significant pain and neurologic symptoms if the nerve root is severely inflamed or compressed. Similarly, a large herniation may cause little to no pain if it does not affect a nerve root.
A lumbar herniated disc – also called a slipped disc, bulging disc, or disc bulge – is a common but complex condition that affects everyone differently.
In This Article:
- Lumbar Herniated Disc: What You Should Know
- Lumbar Herniated Disc Symptoms
- Lumbar Herniated Disc: Causes and Risk Factors
- Diagnosing a Lumbar Herniated Disc
- Treatment for a Lumbar Herniated Disc
- Lumbar Herniated Disc Video
What Causes a Lumbar Disc to Herniate
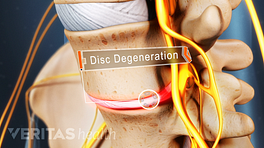
A disc is most likely to herniate if it has lost some or all of its water content, making it brittle and weak.
The most common cause of lumbar disc herniation is disc degeneration – a natural process that occurs with age – leading to dehydration and weakening of the spinal disc.These changes make the disc weak and reduce its ability to act as a shock absorber, making the outer ring more prone to tearing under pressure and the inner core more likely to progressively herniate over time. 1 Al Qaraghli MI, De Jesus O. Lumbar Disc Herniation. [Updated 2023 Aug 14]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK560878/ , 2 Dydyk AM, Ngnitewe Massa R, Mesfin FB. Disc Herniation. [Updated 2023 Jan 16]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK441822/
The second most common cause of a lumbar herniated disc is a sudden injury to the disc, such as while lifting a heavy object or unnaturally twisting the lower back, which results in an immediate tear in the outer layer and herniation of the inner core. 1 Al Qaraghli MI, De Jesus O. Lumbar Disc Herniation. [Updated 2023 Aug 14]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK560878/ , 2 Dydyk AM, Ngnitewe Massa R, Mesfin FB. Disc Herniation. [Updated 2023 Jan 16]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK441822/
How a Herniated Disc Causes Pain
A lumbar disc herniation causes pain in 2 ways:
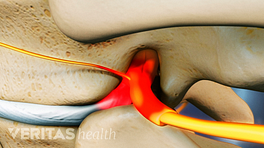
- It inflames or compresses a nearby spinal nerve – causing pain and other symptoms to radiate along the path of the nerve.
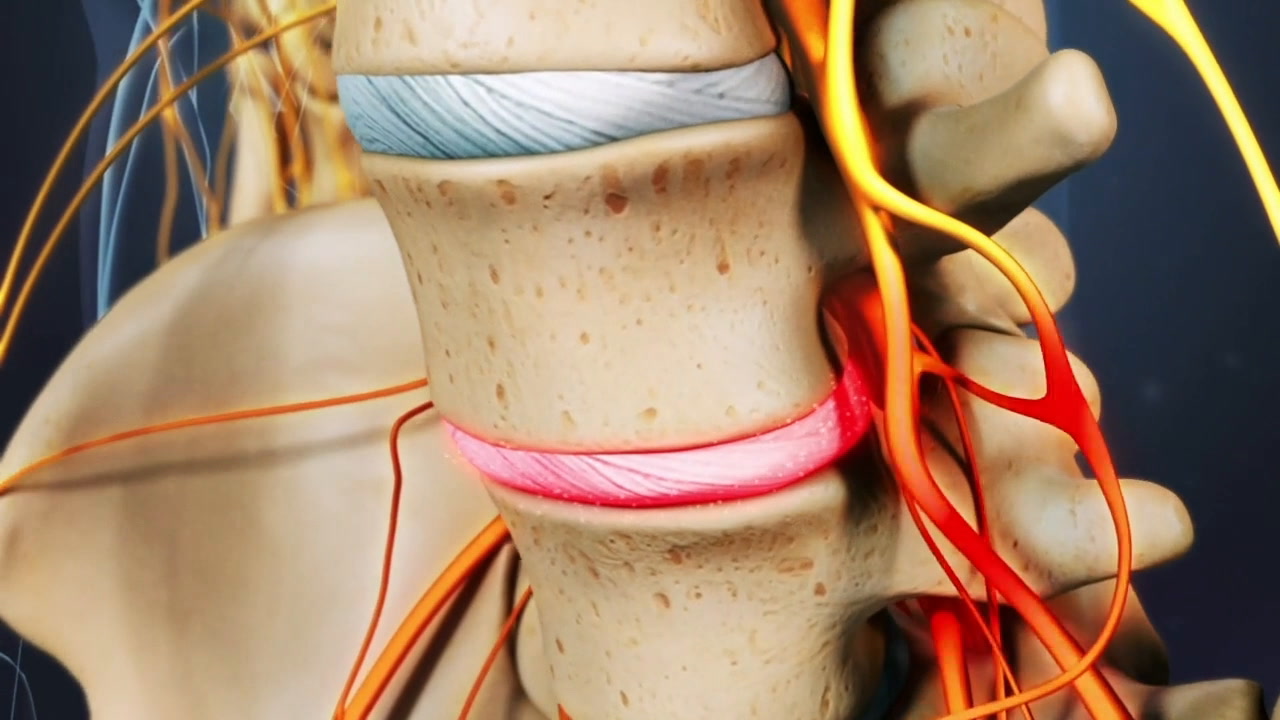
- It presses on the posterior longitudinal ligament – a band of ligament that runs along the length of the spine between the discs and the spinal cord – causing localized pain in the lower back near the area of the herniation.
If the disc material inflames or irritates a nearby spinal nerve root, it causes burning pain, commonly called sciatica, which radiates from the lower back through the buttock and into the leg. Nerve root irritation is primarily caused by inflammatory proteins that leak out of the disc’s inner core and concentrate in the area around the nerve root. 3 Cosamalón-Gan I, Cosamalón-Gan T, Mattos-Piaggio G, Villar-Suárez V, García-Cosamalón J, Vega-Álvarez JA. Inflammation in the intervertebral disc herniation. Neurocirugía (English Edition). 2021;32(1):21-35. doi: 10.1016/j.neucie.2020.04.001 The medical term for sciatica is radicular pain.
If the herniation mechanically compresses the nerve root, it may cause neurologic symptoms and signs, also called lumbar radiculopathy. Symptoms and signs of nerve root compression typically include numbness, a pins and needles sensation, and weakness in the leg and/or foot. Additionally, spinal nerve compression potentially leads to reduced blood flow to the nerve and swelling, further contributing to pain. 1 Al Qaraghli MI, De Jesus O. Lumbar Disc Herniation. [Updated 2023 Aug 14]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK560878/
Watch Sciatica Causes and Symptoms Video
Some disc herniations that exert pressure on the posterior longitudinal ligament also affect the spinal cord or cauda equina – causing more serious symptoms such as loss of sensation in the lower body or problems with walking.
How Long It Takes to Recover from A Herniated Disc
Symptoms of a herniated disc are usually short-lived. In 90% of cases, a herniated disc in the lower back heals on its own within 6 to 12 weeks. 1 Al Qaraghli MI, De Jesus O. Lumbar Disc Herniation. [Updated 2023 Aug 14]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK560878/
Individuals without neurological signs (radiculopathy) tend to recover sooner, sometimes as soon as 2 weeks. 1 Al Qaraghli MI, De Jesus O. Lumbar Disc Herniation. [Updated 2023 Aug 14]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK560878/
Surgery may be considered if the symptoms and/or signs continue or progressively worsen despite several months of non-surgical treatments. 4 Schoenfeld AJ, Weiner BK. Treatment of lumbar disc herniation: Evidence-based practice. Int J Gen Med. 2010;3:209-214. Published 2010 Jul 21. doi:10.2147/ijgm.s12270 In some cases, surgery may be considered sooner or may be an urgent medical necessity, such as in cauda equina syndrome. 1 Al Qaraghli MI, De Jesus O. Lumbar Disc Herniation. [Updated 2023 Aug 14]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK560878/
When a Lumbar Herniated Disc Is a Medical Emergency
Severe pain, numbness, and/or weakness in both legs is a red flag symptom of a herniated disc.
In rare cases, a herniated disc in the lower back compresses the spinal cord or cauda equina – the bundle of spinal nerves extending from the end of the spinal cord – and becomes a medical emergency requiring surgery to prevent permanent neurologic damage. 5 Kapetanakis S, Chaniotakis C, Kazakos C, Papathanasiou JV. Cauda Equina Syndrome Due to Lumbar Disc Herniation: a Review of Literature. Folia Medica. 2017;59(4):377-386. doi: 10.1515/folmed-2017-0038 , 6 Endo F, Iizuka H, Iizuka Y, Kobayashi R, Mieda T, Takagishi K. Myelopathy due to lumbar disc herniation in the presence of a tethered cord. Spinal Cord. 2014;52(1):S11-S13. doi:10.1038/sc.2014.67
Symptoms and signs to watch for include 7 Bednar DA. Cauda equina syndrome from lumbar disc herniation. CMAJ. 2016;188(4):284. doi:10.1503/cmaj.150206 :
- Severe, disabling pain in both legs
- Numbness in the inner thighs, the back of the legs, and the area around the rectum (saddle anesthesia)
- Progressive weakness or motor deficits in the legs, ankles, or feet making it difficult to walk or stand
- Bladder and/or bowel dysfunction
- Sexual dysfunction (such as the inability to get or maintain an erection or loss of sensation in the genital area)
Paralysis and permanent nerve damage are possible if treatment is delayed. Emergency medical care is needed if these symptoms occur. 5 Kapetanakis S, Chaniotakis C, Kazakos C, Papathanasiou JV. Cauda Equina Syndrome Due to Lumbar Disc Herniation: a Review of Literature. Folia Medica. 2017;59(4):377-386. doi: 10.1515/folmed-2017-0038
Read more about Cauda Equina Syndrome Symptoms
Doctors Who Diagnose and Treat Herniated Discs
In addition to primary care physicians, specialists who diagnose and treat lumbar spine problems include:
- Physiatrist (Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation specialist)
- Orthopedic or neurological spine surgeon
- Neurologist
- Chiropractor
- Physical therapist
A lumbar herniated disc does not always cause pain or serious complications. In fact, in up to 99% of cases, the injured disc does not cause symptoms, and the herniation is only discovered during imaging tests (such as magnetic resonance imaging) for unrelated medical problems. 2 Dydyk AM, Ngnitewe Massa R, Mesfin FB. Disc Herniation. [Updated 2023 Jan 16]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK441822/
- 1 Al Qaraghli MI, De Jesus O. Lumbar Disc Herniation. [Updated 2023 Aug 14]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK560878/
- 2 Dydyk AM, Ngnitewe Massa R, Mesfin FB. Disc Herniation. [Updated 2023 Jan 16]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK441822/
- 3 Cosamalón-Gan I, Cosamalón-Gan T, Mattos-Piaggio G, Villar-Suárez V, García-Cosamalón J, Vega-Álvarez JA. Inflammation in the intervertebral disc herniation. Neurocirugía (English Edition). 2021;32(1):21-35. doi: 10.1016/j.neucie.2020.04.001
- 4 Schoenfeld AJ, Weiner BK. Treatment of lumbar disc herniation: Evidence-based practice. Int J Gen Med. 2010;3:209-214. Published 2010 Jul 21. doi:10.2147/ijgm.s12270
- 5 Kapetanakis S, Chaniotakis C, Kazakos C, Papathanasiou JV. Cauda Equina Syndrome Due to Lumbar Disc Herniation: a Review of Literature. Folia Medica. 2017;59(4):377-386. doi: 10.1515/folmed-2017-0038
- 6 Endo F, Iizuka H, Iizuka Y, Kobayashi R, Mieda T, Takagishi K. Myelopathy due to lumbar disc herniation in the presence of a tethered cord. Spinal Cord. 2014;52(1):S11-S13. doi:10.1038/sc.2014.67
- 7 Bednar DA. Cauda equina syndrome from lumbar disc herniation. CMAJ. 2016;188(4):284. doi:10.1503/cmaj.150206