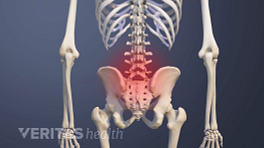
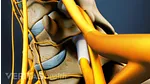
Basivertebral nerve ablation is a treatment option for chronic back pain caused by damaged vertebral endplates in the lumbar spine (lower back). 1 Tieppo Francio V, Sayed D. Basivertebral Nerve Ablation. [Updated 2023 May 22]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK572127/
This procedure may be recommended for those with moderate to severe low back pain who have specific endplate changes identified on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). These changes are usually seen at the L3-L4, L4-L5, and L5-S1 lumbar spine segments. 1 Tieppo Francio V, Sayed D. Basivertebral Nerve Ablation. [Updated 2023 May 22]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK572127/
In This Article:
- Basivertebral Nerve Ablation for Lower Back Pain
- Basivertebral Nerve Ablation Explained Step-by-Step
- Basivertebral Nerve Ablation Animation
What Is a Basivertebral Nerve Ablation?
This procedure creates a heat lesion on the nerve, which supplies sensation to the injured endplate – the basivertebral nerve – to block pain signals and provide long-lasting pain relief. 1 Tieppo Francio V, Sayed D. Basivertebral Nerve Ablation. [Updated 2023 May 22]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK572127/
The essentials of basivertebral nerve ablation are:
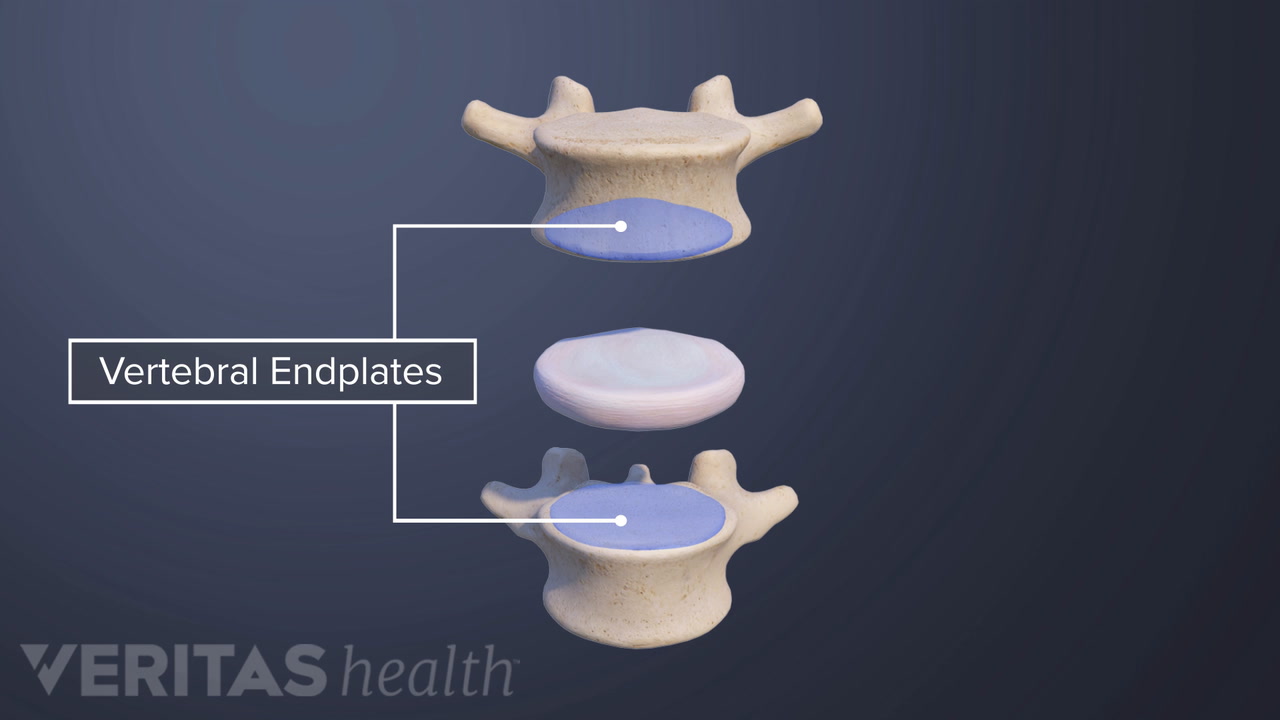
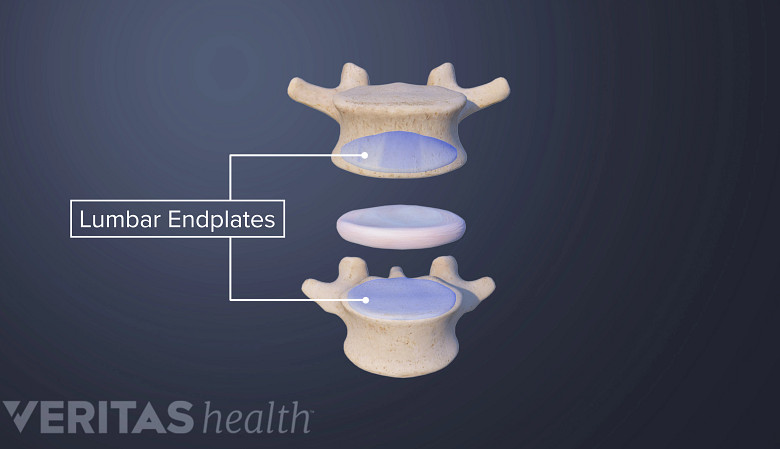
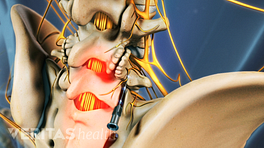
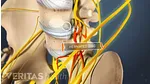
- The vertebral endplate is a thin structure made up of cartilage and bone connecting each vertebra – the cylindrical bony building blocks of the spine – and the adjacent spinal disc – the cushion-like structure providing shock absorption.
- The basivertebral nerve lies within the vertebra and branches into a cluster of nerve fibers within these vertebral endplates.
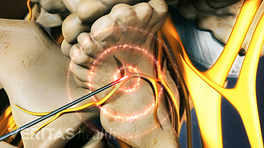
- Ablation is a type of procedure in which a thin needle-like device is inserted into the targeted area, and heat is applied to destroy a small section of nerve tissue, preventing the nerve from communicating the pain sensation from the damaged endplate to the brain. 2 Wray JK, Dixon B, Przkora R. Radiofrequency Ablation. [Updated 2023 Jun 12]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482387/
This ablation procedure involves inserting the device into the bone of the vertebra (intraosseous) and targeting the area of the nerve where it begins to branch. 1 Tieppo Francio V, Sayed D. Basivertebral Nerve Ablation. [Updated 2023 May 22]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK572127/
Alternative names for basivertebral nerve ablation include:
- Basivertebral radiofrequency ablation because the heating mechanism is a radiofrequency probe.
- BVN ablation (BVN is short for basivertebral nerve)
- IntraceptTM is the brand name of the device used in this procedure.
As noted above, the basivertebral nerve may also be referred to by its acronym “BVN.”
How Vertebral Endplates Cause Pain
Endplates are highly susceptible to damage from wear and tear from everyday activities.
Vertebral endplates are a common source of chronic lower back pain. Research shows up to 43% of patients with chronic lower back pain have vertebral endplate damage. 1 Tieppo Francio V, Sayed D. Basivertebral Nerve Ablation. [Updated 2023 May 22]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK572127/
Pain that is caused by damaged endplates is called vertebrogenic pain. 1 Tieppo Francio V, Sayed D. Basivertebral Nerve Ablation. [Updated 2023 May 22]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK572127/
Understanding vertebral endplates
Vertebral endplates are situated between the vertebral body and intervertebral disc.
The endplates have a complex anatomy and provide several functions:
- Each endplate comprises 2 layers – the bony layer attaches to the vertebral body, and the cartilaginous layer is affixed to the spinal disc.
- The rigid bony layer of the endplates provides support and protection for the vertebrae.
- The pliable layer of cartilage allows for transporting nutrients and fluid into the disc.
The competing structural needs of the endplate layers and the stress on these structures make them highly susceptible to damage from wear and tear over time, such as from everyday bending, twisting, and lifting, many sports, physically demanding jobs, and natural aging processes. 3 Nwosu M, Agyeman WY, Bisht A, et al. The Effectiveness of Intraosseous Basivertebral Nerve Ablation in the Treatment of Nonradiating Vertebrogenic Pain: A Systematic Review. Cureus. 2023;15(4):e37114. Published 2023 Apr 4. doi:10.7759/cureus.37114
How endplates generate pain
Spinal conditions such as lumbar degenerative disc disease are known to cause endplate damage.
When a vertebral endplate becomes damaged, basivertebral nerve fibers transmit pain signals to the brain. Injury also triggers inflammation, further damaging the endplate and worsening pain. 1 Tieppo Francio V, Sayed D. Basivertebral Nerve Ablation. [Updated 2023 May 22]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK572127/
Common spinal conditions known to cause endplate damage include 4 Koreckij T, Kreiner S, Khalil JG, et al. Prospective, randomized, multicenter study of intraosseous basivertebral nerve ablation for the treatment of chronic low back pain: 24-Month treatment arm results. N Am Spine Soc J. 2021;8:100089. Published 2021 Oct 26. doi:10.1016/j.xnsj.2021.100089 :
Basivertebral nerves are sensitized if these conditions cause direct injury to the endplate tissue or place excessive mechanical force on the endplate. 2 Wray JK, Dixon B, Przkora R. Radiofrequency Ablation. [Updated 2023 Jun 12]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482387/ , 3 Nwosu M, Agyeman WY, Bisht A, et al. The Effectiveness of Intraosseous Basivertebral Nerve Ablation in the Treatment of Nonradiating Vertebrogenic Pain: A Systematic Review. Cureus. 2023;15(4):e37114. Published 2023 Apr 4. doi:10.7759/cureus.37114
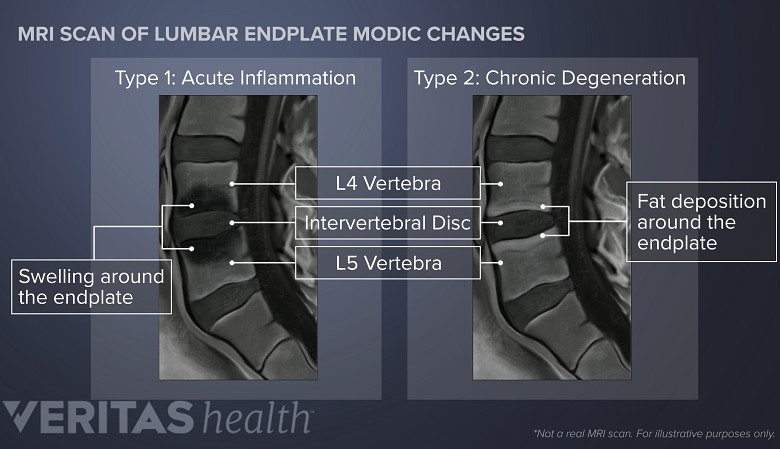
Modic changes in vertebral endplates
Basivertebral nerve ablation is performed in patients with Modic Type 1 and Type 2 changes.
Changes in the structure of vertebral endplates caused by damage and inflammation create distinctive patterns visible on an MRI scan known as Modic changes. 1 Tieppo Francio V, Sayed D. Basivertebral Nerve Ablation. [Updated 2023 May 22]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK572127/ , 5 Viswanathan VK, Shetty AP, Rajasekaran S. Modic changes - An evidence-based, narrative review on its patho-physiology, clinical significance and role in chronic low back pain. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2020;11(5):761-769. doi:10.1016/j.jcot.2020.06.025 , 6 Lambrechts MJ, Issa TZ, Toci GR, et al. Modic Changes of the Cervical and Lumbar Spine and Their Effect on Neck and Back Pain: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Global Spine J. 2023;13(5):1405-1417. doi:10.1177/21925682221143332
Modic changes are categorized into 3 main types based on their appearance on MRI scans and correlate to the nature of endplate injury. 4 Koreckij T, Kreiner S, Khalil JG, et al. Prospective, randomized, multicenter study of intraosseous basivertebral nerve ablation for the treatment of chronic low back pain: 24-Month treatment arm results. N Am Spine Soc J. 2021;8:100089. Published 2021 Oct 26. doi:10.1016/j.xnsj.2021.100089 , 5 Viswanathan VK, Shetty AP, Rajasekaran S. Modic changes - An evidence-based, narrative review on its patho-physiology, clinical significance and role in chronic low back pain. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2020;11(5):761-769. doi:10.1016/j.jcot.2020.06.025
Basivertebral nerve ablation is primarily performed in patients with:
- Modic Type 1 (acute inflammation) or
- Modic Type 2 (chronic degeneration) changes. 7 Conger A, Schuster NM, Cheng DS, et al. The Effectiveness of Intraosseous Basivertebral Nerve Radiofrequency Neurotomy for the Treatment of Chronic Low Back Pain in Patients with Modic Changes: A Systematic Review. Pain Med. 2021;22(5):1039-1054. doi:10.1093/pm/pnab040
BVN Ablation Treatment Goals
The primary goals of basivertebral nerve ablation are 3 Nwosu M, Agyeman WY, Bisht A, et al. The Effectiveness of Intraosseous Basivertebral Nerve Ablation in the Treatment of Nonradiating Vertebrogenic Pain: A Systematic Review. Cureus. 2023;15(4):e37114. Published 2023 Apr 4. doi:10.7759/cureus.37114 , 8 Lotz JC, Fields AJ, Liebenberg EC. The role of the vertebral end plate in low back pain. Global Spine J. 2013;3(3):153-164. doi:10.1055/s-0033-1347298 :
- Long-term pain relief
- Avoidance of surgery
The procedure is a form of pain management and does not cure the underlying cause of pain or repair endplate damage.
Improving low back pain allows patients to engage in rehabilitative activities such as exercise, physical therapy, and postural modifications, creating an optimal healing environment and helping prevent further endplate damage and/or disc degeneration.
Effectiveness of Basivertebral Nerve Ablation
Like most treatments for lower back pain, the success rates of an endplate injection are variable. Current research shows:
- More than half of patients who undergo a basivertebral nerve ablation experience significant pain relief and functional improvement. 2 Wray JK, Dixon B, Przkora R. Radiofrequency Ablation. [Updated 2023 Jun 12]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482387/
- Symptoms begin to improve for most patients within 2 to 6 weeks of the procedure, with maximum benefit felt at around 3 to 6 months. 2 Wray JK, Dixon B, Przkora R. Radiofrequency Ablation. [Updated 2023 Jun 12]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482387/ , 6 Lambrechts MJ, Issa TZ, Toci GR, et al. Modic Changes of the Cervical and Lumbar Spine and Their Effect on Neck and Back Pain: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Global Spine J. 2023;13(5):1405-1417. doi:10.1177/21925682221143332
- Approximately 35% of patients have complete resolution of pain. 2 Wray JK, Dixon B, Przkora R. Radiofrequency Ablation. [Updated 2023 Jun 12]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482387/ , 6 Lambrechts MJ, Issa TZ, Toci GR, et al. Modic Changes of the Cervical and Lumbar Spine and Their Effect on Neck and Back Pain: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Global Spine J. 2023;13(5):1405-1417. doi:10.1177/21925682221143332
Studies have focused primarily on the effects of this procedure on lower back pain and functional status in patients without additional spinal complications. 9 Urits I, Noor N, Johal AS, et al. Basivertebral Nerve Ablation for the Treatment of Vertebrogenic Pain. Pain Ther. 2021;10(1):39-53. doi:10.1007/s40122-020-00211-2
More research is needed to establish the benefit and safety of basivertebral nerve ablation when endplate damage is seen in patients with radicular pain in the lower extremities (sciatica).
Several variables influence the success rates of the procedure, such as:
- Accurate clinical diagnosis of vertebrogenic pain
- Skill and experience of the physician performing the procedure
- The patient’s overall health status
- The patient’s lifestyle factors, such as smoking/nicotine intake and fitness level
Adherence to physical therapy and rehabilitation recommendations following the procedure also contributes to the degree of pain relief and functional improvement following this procedure.
Effectiveness compared to standard treatments
One study has demonstrated that basivertebral nerve ablation provides pain relief for more patients compared to the nonsurgical standard of care – typically some combination of pain medications, epidural steroid injections, and facet joint procedures. 9 Urits I, Noor N, Johal AS, et al. Basivertebral Nerve Ablation for the Treatment of Vertebrogenic Pain. Pain Ther. 2021;10(1):39-53. doi:10.1007/s40122-020-00211-2 , 10 National Library of Medicine. INTRACEPT: Prospective, Randomized, Multi-center Study Intraosseous Basivertebral Nerve Ablation for Treatment of CLBP (CLBP). Clinicaltrials.gov. Updated August 1, 2023. Accessed October 24, 2023. https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT03246061
Additional studies have shown significant and sustained pain relief and functional improvement in patients with inadequate or “failed” responses to prior spinal injection treatments. 2 Wray JK, Dixon B, Przkora R. Radiofrequency Ablation. [Updated 2023 Jun 12]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482387/
Long-term outcomes
While basivertebral nerve ablation is a newer procedure, results of studies to date show the potential for long-lasting pain relief.
- Improvements in pain and function last up to 2 years after the procedure for 50% to 70% of patients 3 Nwosu M, Agyeman WY, Bisht A, et al. The Effectiveness of Intraosseous Basivertebral Nerve Ablation in the Treatment of Nonradiating Vertebrogenic Pain: A Systematic Review. Cureus. 2023;15(4):e37114. Published 2023 Apr 4. doi:10.7759/cureus.37114
- One study has demonstrated lasting efficacy at 5 years 6 Lambrechts MJ, Issa TZ, Toci GR, et al. Modic Changes of the Cervical and Lumbar Spine and Their Effect on Neck and Back Pain: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Global Spine J. 2023;13(5):1405-1417. doi:10.1177/21925682221143332
Additional research is needed to fully understand the potential benefits, risks, and long-term pain reduction and safety issues.
Who May Be a Candidate
Individuals with damaged endplates and vertebrogenic pain may opt for BVN ablation treatment.
Individuals with severe lower back pain who meet the following criteria are considered for basivertebral nerve ablation 1 Tieppo Francio V, Sayed D. Basivertebral Nerve Ablation. [Updated 2023 May 22]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK572127/ :
- Lower back pain lasting 6 months or longer
- Inadequate response to non-surgical therapies such as pain-relieving medications and physical therapy
- Functional impairment
- Confirmation of skeletal maturity on imaging, meaning the bones have stopped growing
- Modic Type 1 or Type 2 changes on MRI in the lumbar region
If patients cannot undergo an MRI, alternative imaging methods, such as computed tomography (CT) and single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT), can detect vertebral endplate changes. 4 Koreckij T, Kreiner S, Khalil JG, et al. Prospective, randomized, multicenter study of intraosseous basivertebral nerve ablation for the treatment of chronic low back pain: 24-Month treatment arm results. N Am Spine Soc J. 2021;8:100089. Published 2021 Oct 26. doi:10.1016/j.xnsj.2021.100089
Contraindications and Precautions
Basivertebral nerve ablation is not recommended when the risk of complications is significantly increased, including 1 Tieppo Francio V, Sayed D. Basivertebral Nerve Ablation. [Updated 2023 May 22]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK572127/ :
- Systemic and/or spinal infection, such as osteomyelitis
- Pregnancy
- Children and adolescents (due to incomplete spinal maturity)
- Pacemakers and/or implanted defibrillators
- Severe cardiopulmonary disease (such as heart failure or chronic obstructive pulmonary disorder)
It is also recommended to avoid this procedure when hardware, such as pedicle screws or rods, from previous spinal surgery is present in the targeted ablation area, or an alternative is to consider hardware removal before this procedure. 1 Tieppo Francio V, Sayed D. Basivertebral Nerve Ablation. [Updated 2023 May 22]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK572127/
Medical conditions requiring additional precautions
Greater caution is recommended in several conditions due to the potential for injury and/or difficulty performing the ablation 1 Tieppo Francio V, Sayed D. Basivertebral Nerve Ablation. [Updated 2023 May 22]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK572127/ :
- Osteoporosis
- Metastatic cancer or malignant spinal tumor
- Bleeding disorders
- Morbid obesity (BMI greater than 40)
The safety of vertebral endplate injection procedures in various medical conditions has yet to be adequately researched. 1 Tieppo Francio V, Sayed D. Basivertebral Nerve Ablation. [Updated 2023 May 22]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK572127/
As with any invasive procedure, eligibility for basivertebral nerve ablation is impacted by general health status, severe heart or lung conditions, or any concerns that would affect the administration of anesthesia or sedating medications.
Doctors Who Perform Basivertebral Nerve Ablations
The following types of physicians who specialize and are board-certified in Pain Management may be consulted to perform the initial assessment and procedure:
- Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation (Physiatrist)
- Interventional Radiologist
- Anesthesiologist
- Orthopedic spine surgeon
- Neurosurgeon
- Neurologist
In addition to Board Certification in Pain Management, specialized training in patient selection, procedural technique, and follow-up care for basivertebral nerve ablation is required.
- 1 Tieppo Francio V, Sayed D. Basivertebral Nerve Ablation. [Updated 2023 May 22]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK572127/
- 2 Wray JK, Dixon B, Przkora R. Radiofrequency Ablation. [Updated 2023 Jun 12]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482387/
- 3 Nwosu M, Agyeman WY, Bisht A, et al. The Effectiveness of Intraosseous Basivertebral Nerve Ablation in the Treatment of Nonradiating Vertebrogenic Pain: A Systematic Review. Cureus. 2023;15(4):e37114. Published 2023 Apr 4. doi:10.7759/cureus.37114
- 4 Koreckij T, Kreiner S, Khalil JG, et al. Prospective, randomized, multicenter study of intraosseous basivertebral nerve ablation for the treatment of chronic low back pain: 24-Month treatment arm results. N Am Spine Soc J. 2021;8:100089. Published 2021 Oct 26. doi:10.1016/j.xnsj.2021.100089
- 5 Viswanathan VK, Shetty AP, Rajasekaran S. Modic changes - An evidence-based, narrative review on its patho-physiology, clinical significance and role in chronic low back pain. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2020;11(5):761-769. doi:10.1016/j.jcot.2020.06.025
- 6 Lambrechts MJ, Issa TZ, Toci GR, et al. Modic Changes of the Cervical and Lumbar Spine and Their Effect on Neck and Back Pain: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Global Spine J. 2023;13(5):1405-1417. doi:10.1177/21925682221143332
- 7 Conger A, Schuster NM, Cheng DS, et al. The Effectiveness of Intraosseous Basivertebral Nerve Radiofrequency Neurotomy for the Treatment of Chronic Low Back Pain in Patients with Modic Changes: A Systematic Review. Pain Med. 2021;22(5):1039-1054. doi:10.1093/pm/pnab040
- 8 Lotz JC, Fields AJ, Liebenberg EC. The role of the vertebral end plate in low back pain. Global Spine J. 2013;3(3):153-164. doi:10.1055/s-0033-1347298
- 9 Urits I, Noor N, Johal AS, et al. Basivertebral Nerve Ablation for the Treatment of Vertebrogenic Pain. Pain Ther. 2021;10(1):39-53. doi:10.1007/s40122-020-00211-2
- 10 National Library of Medicine. INTRACEPT: Prospective, Randomized, Multi-center Study Intraosseous Basivertebral Nerve Ablation for Treatment of CLBP (CLBP). Clinicaltrials.gov. Updated August 1, 2023. Accessed October 24, 2023. https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT03246061